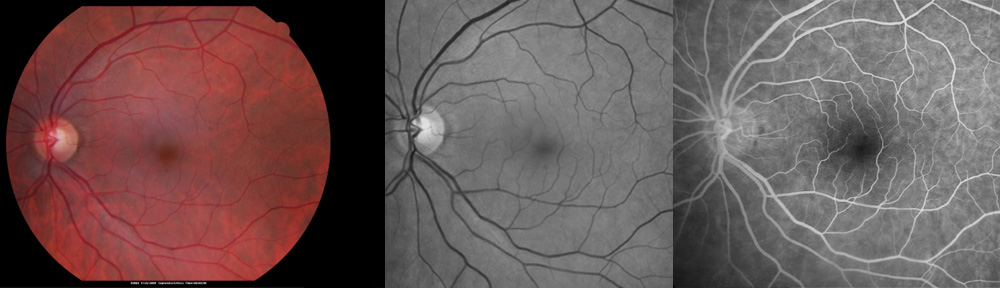
What is macular telangiectasia (MacTel)?
Macular telangiectasia is a disorder of retinal cells and tiny blood vessels located in the center of the retina. It has also been called juxtafoveal telangiectasis. The retina in your eye is like the film inside a camera. The retina “takes the picture” of objects you look at and sends the message to the brain. The macula is the central portion of the retina that is responsible for sharp reading vision. In MacTel the macula undergoes slow degeneration, and tiny foveal blood vessels become irregular and dilated for unknown reasons. They rarely leak blood or clear fluid in the fovea. MacTel may resemble changes in the retina from drugs that are used to treat breast cancer (Tamoxifen).
Who is at risk for developing macular telangiectasia?
Macular telangiectasia is usually found in males and females during their 5th to 8th decade of life. It may occur in as many as one in every 1,000 persons. MacTel is associated with diabetes, high blood pressure, and tobacco use, but the exact cause has not been determined. Hereditary factors appear significant. Low serum levels of an amino acid called L-serine may play a role, but there are no clear recommendations for supplementation to date.
What are the symptoms of macular telangiectasia?
Blurring of vision is the most common symptom. Distortion of vision may also make reading or seeing small details difficult. Distortion is when straight lines appear wavy or crooked. It may be monitored with the Amsler grid test. Symptoms and clarity of vision may change from day to day. If sudden loss of vision or increased distortion occurs, your doctor should be notified without delay (within a week) as treatment may be needed.
What treatment is available?
There is no cure, but treatment may improve vision or keep the vision from worsening in certain instances. No specific treatment may be recommended if the symptoms are mild. Supplements containing the amino acid L-serine are being investigated. Laser and medicine injections help selected patients. Treatment usually does not return the vision to normal.
Your doctor is going to order appropriate tests and recommend the best course of action to take at this time. Physical activity and use of your eyes will not worsen macular telangiectasia. Magnification may help with reading. If you have any questions, please feel free to ask. If you would like to participate in research, contact www.mactelresearch.com.
For a telemedicine consultation with Dr Pautler, please send email request to spautler@rvaf.com. We accept Medicare and most insurances in Florida. Please include contact information (including phone number) in the email. We are unable to provide consultation for those living outside the state of Florida with the exception of limited one-time consultations with residents of the following states: Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Georgia, Minnesota, and Washington.
Copyright © 2014-2022 Designs Unlimited of Florida. All Rights Reserved.